Fiber optic cables are the backbone of modern digital communication, transmitting vast amounts of data at high speed over long distances with minimal signal loss. As networks demand higher bandwidth and faster connections, understanding what a fiber optic cable is becomes essential for technical decision-makers and business stakeholders alike.
What Is a Fiber Optic Cable?
A fiber optic cable is a type of data transmission medium that uses light signals instead of electrical signals to carry information. Unlike copper cables, which transmit data via electrical pulses, fiber optic cables rely on internal reflection of light within ultra-thin glass or plastic fibers. This allows data to travel at near-light speeds with minimal attenuation.
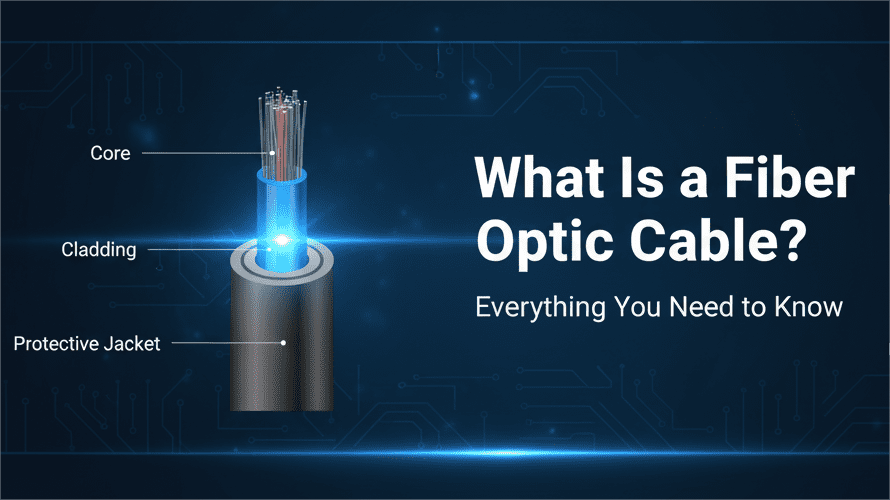
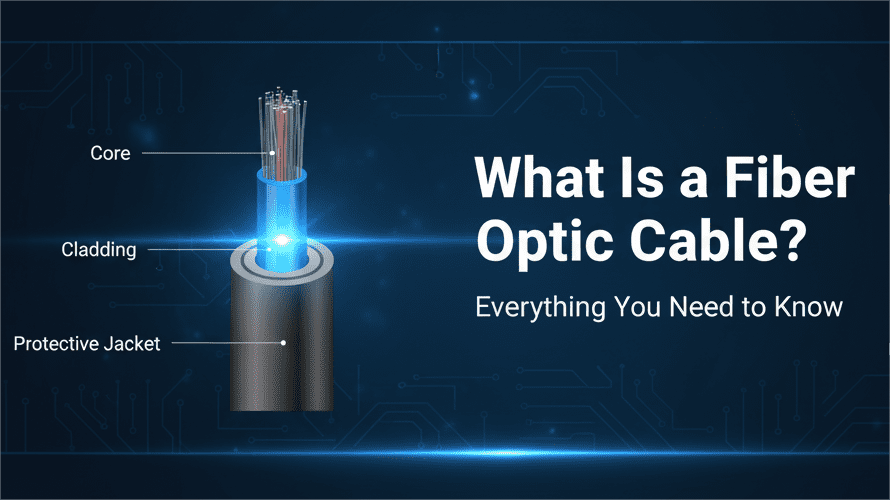
Fiber optic cables typically consist of several components:
- Core: The central glass or plastic fiber that carries the light signal.
- Cladding: Surrounds the core and reflects light back into it, preventing signal loss.
- Protective Jacket: Shields fibers from environmental damage, moisture, and physical stress.
- Additional Layers: May include strength members for tensile support and buffer coatings for flexibility and protection.
Types of Fiber Optic Cables

Fiber optic cables are classified by mode, construction, and application:
1. By Mode
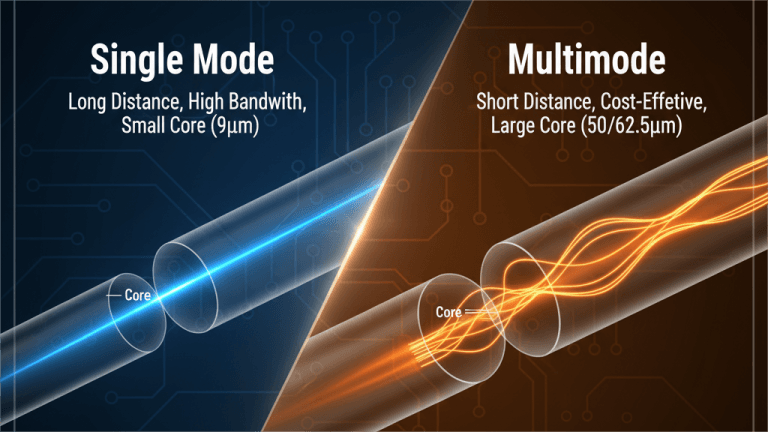
- Single-Mode Fiber (SMF):
- Core diameter: ~8–10 µm
- Transmits a single light mode, ideal for long-distance, high-bandwidth networks.
- Commonly used in backbone networks, telecom, and long-haul data centers.
- Multimode Fiber (MMF):
- Core diameter: ~50–62.5 µm
- Supports multiple light modes, suited for short-distance communication such as LANs, campus networks, or intra-data center connections.
2. By Construction
- Loose Tube Fiber: Fibers are loosely packed in tubes filled with gel or air for outdoor environments, protecting against moisture and extreme temperatures.
- Tight-Buffered Fiber: Fibers are coated directly with protective layers, suitable for indoor environments and easier installation in patch panels or short cable runs.
3. By Application
- Indoor Cables: Structured cabling, office, and data-center environments.
- Outdoor Cables: Armored or loose-tube designs for underground, aerial, or long-distance deployments.
- Hybrid Cables: Suitable for both indoor and outdoor use for flexible deployments.
How Fiber Optic Cables Work
Fiber optic cables transmit data by converting electrical signals into light signals using lasers or LEDs. The light travels through the core, reflecting internally off the cladding due to total internal reflection, until it reaches a receiver, which converts it back into electrical signals.
This technology provides:
- High bandwidth capacity – hundreds of times more than copper cables
- Low signal loss – longer distances without repeaters
- Immunity to electromagnetic interference – essential for industrial and telecom applications
Why Fiber Optic Cables Are Critical
Fiber optic cables are essential because they provide:
- Speed & Performance: Supports ultra-fast transmission for cloud computing, video streaming, and 5G networks
- Reliability: Resistant to interference, corrosion, and environmental hazards
- Scalability: Capable of handling future network growth without major infrastructure upgrades
- Security: Difficult to tap, ideal for sensitive communications
PHILISUN Fiber Optic Cable Solutions

| Feature | PHILISUN Advantage |
| Precision Engineering | Low insertion loss, high return loss, consistent optical performance |
| Product Range | Single-mode, multimode, indoor, outdoor, hybrid |
| Customization | Length, jacket type, fiber count, and connector type tailored to client’s needs |
| High-Quality Connectors | MPO/MTP, LC, SC, APC connectors with precise polishing |
| Quality Assurance | Rigorous optical and mechanical testing for reliability |
PHILISUN cables support data centers, telecom infrastructure, and enterprise networks, meeting strict industry standards.
Applications of Fiber Optic Cables
- Data Centers & Cloud Infrastructure: High-speed backbone links and intra-rack connectivity
- Telecommunication Networks: Long-distance trunk lines and metropolitan networks
- Enterprise Networks: LANs, campus networks, and office connectivity
- Industrial & Smart City Projects: Reliable communication in challenging environments
- 5G & Edge Computing: Low-latency, high-bandwidth transport for modern wireless networks
Choosing the Right Fiber Optic Cable
Consider the following when selecting a fiber optic cable:
- Distance & Bandwidth Requirements: Single-mode for long haul, multimode for short haul
- Installation Environment: Indoor, outdoor, or hybrid
- Connector Type: LC, SC, MPO/MTP, or APC, depending on devices
- Durability & Protection: LSZH jackets for indoor safety, armored for outdoor ruggedness
PHILISUN provides expert guidance to help clients choose, configure, and deploy the optimal fiber optic solution for their network.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the difference between single-mode and multimode fiber optic cables?
A: Single-mode fiber has a smaller core (~8–10 µm) for long-distance, high-speed transmission, while multimode fiber has a larger core (~50–62.5 µm) for short-distance applications such as LANs and intra-data center connections.
Q2: Can fiber optic cables be used both indoors and outdoors?
A: Yes. Indoor cables are designed for offices and structured cabling, while outdoor cables are armored or loose-tube to withstand environmental conditions. Hybrid cables can serve both environments.
Q3: How does a fiber optic cable transmit data?
A: Fiber optic cables convert electrical signals into light using lasers or LEDs. Light travels through the fiber core by internal reflection, then is converted back into electrical signals at the receiver.
Q4: Why choose PHILISUN fiber optic cables?
A: PHILISUN offers high-quality, precision-engineered fiber optic cables, customizable lengths and connectors, and rigorous testing for reliable performance across data centers, telecom, and enterprise networks.
Q5: How do I choose the right fiber optic cable for my network?
A: Consider distance, bandwidth, installation environment, connector type, and durability. PHILISUN provides consultation to ensure the best solution for your network.
Conclusion
A fiber optic cable is more than a conduit for data — it is the foundation of modern, high-speed, reliable networks. With PHILISUN’s comprehensive range of fiber solutions, organizations can future-proof connectivity, meeting today’s bandwidth demands while enabling growth for tomorrow.
For businesses looking to upgrade or expand optical networks, PHILISUN provides trusted, high-performance fiber optic cables for any application — from data centers and telecom to enterprise and industrial deployments.
Future-proof your connectivity. Contact PHILISUN now and get the fiber solution your network deserves.