In the world of high-speed communication, precision is everything. Whether it’s data centers, enterprise networks, or telecom backbones, one of the most overlooked yet critical aspects of fiber optic management is color coding. The fiber optic color code system provides a universal language for identifying fibers, cables, and connectors — ensuring that installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting are fast and error-free.
As a fiber optic manufacturer, PHILISUN follows the highest international standards for fiber identification, offering well-labeled, easy-to-manage cable systems designed for seamless operation.

What Is the Fiber Optic Color Code?
A fiber optic color code is a standardized method for identifying individual fibers, buffer tubes, connectors, and outer jackets. This code helps technicians distinguish between hundreds — even thousands — of fibers inside a large optical cable.
The most widely used international standard is TIA-598-C, which defines the colors for:
- Individual fiber strands
- Buffer tubes
- Outer cable jackets
- Connector boots and adapters
By following these color codes, engineers can trace and connect fibers efficiently, avoiding confusion during installations or repairs.
The Standard 12-Color Fiber Sequence
According to the TIA-598-C standard, fiber strands inside a cable follow this 12-color pattern:
| Number | Color | Number | Color |
| 1 | Blue | 7 | Red |
| 2 | Orange | 8 | Black |
| 3 | Green | 9 | Yellow |
| 4 | Brown | 10 | Violet |
| 5 | Slate (Gray) | 11 | Rose |
| 6 | White | 12 | Aqua |
When a cable contains more than 12 fibers, the sequence repeats — each group is bundled in a differently colored buffer tube for easy identification.
Fiber Jacket Color Codes by Type
The outer jacket color also indicates the fiber type — helping technicians quickly identify single-mode or multimode cables.
| Fiber Type | Common Jacket Color | Typical Use |
| Single-mode (OS1/OS2) | Yellow | Long-distance telecom and data center backbones |
| Multimode (OM1/OM2) | Orange | Short-range LAN or patch cables |
| Multimode (OM3/OM4) | Aqua | High-speed 10G/40G/100G networks |
| Wideband Multimode (OM5) | Lime Green | 400G+ and SWDM applications |
(Source: TIA-598-C and ISO/IEC 11801 standards)
Connector and Adapter Color Codes
Fiber optic connectors and adapters also follow color conventions based on connector type and polish angle.
| Connector Type | Polish | Typical Color | Application |
| SC/LC/FC UPC | Ultra Physical Contact | Blue | Standard single-mode use |
| SC/LC/FC APC | Angled Physical Contact | Green | Low-reflection single-mode |
| SC/LC MM (OM1/OM2) | Physical Contact | Beige | Legacy multimode systems |
| SC/LC MM (OM3/OM4) | Physical Contact | Aqua | High-bandwidth multimode |
| SC/LC MM (OM5) | Physical Contact | Lime Green | Wideband multimode fiber |
These visual identifiers prevent mixing different fiber types or polish types — which could cause performance loss or reflection issues.
Color Coding for Buffer Tubes and Loose Tube Cables
In loose-tube designs, each buffer tube holds up to 12 fibers that follow the same 12-color sequence.
If a cable has more than 12 fibers, additional tubes repeat the sequence but use different tube jacket colors, typically blue, orange, green, brown, or slate.
This organization ensures fast identification, even in cables with 144 or 288 fibers.
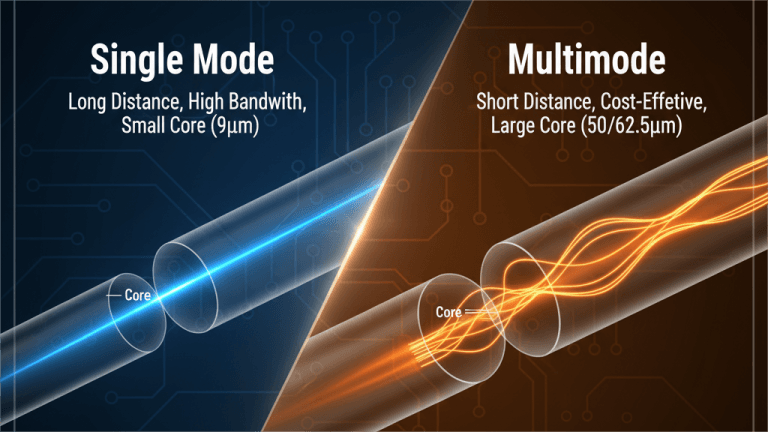
What’s the Difference Between Single-Mode and Multimode Fiber?
| Feature | Single-Mode Fiber | Multimode Fiber |
| Core Size | ~9 µm | 50 µm (OM2–OM5), 62.5 µm (OM1) |
| Light Source | Laser | LED or VCSEL |
| Distance Range | Up to 80 km+ | Typically < 550 m |
| Jacket Color | Yellow | Orange / Aqua / Lime Green |
| Use Case | Long-haul telecom, backbone networks | Local data centers, LANs, short-distance links |
Single-mode fibers carry a single light path for ultra-long distances, while multimode fibers allow multiple light modes for cost-effective short links.
Advantages of Using Fiber Color Coding
- Quick Fiber Identification – Simplifies large-scale installations.
- Efficient Maintenance – Reduces downtime by minimizing confusion.
- Improved Safety – Prevents accidental disconnections or wrong patching.
- Standardization – Ensures compatibility across regions and systems.
- Better Documentation – Helps record and maintain accurate fiber maps.
PHILISUN implements these principles across its production line, ensuring that every cable is color-accurate, clearly labeled, and compliant with TIA and IEC standards.
Applications of Fiber Color Coding
- Data Centers: Managing thousands of connections efficiently.
- Telecom Networks: Simplifying splicing and routing for multi-fiber trunks.
- Campus & Enterprise Networks: Easy upgrades and tracing during expansion.
- Industrial Systems: Reliable maintenance under demanding conditions.
FAQs: Fiber Optic Color Code Explained
1. Why are fiber optic cables color-coded?
Color coding helps identify fibers quickly, especially in cables containing many strands. It improves organization, safety, and maintenance efficiency.
2. What is the difference between buffer color and jacket color?
The buffer color identifies the fiber’s order inside the cable, while the jacket color identifies the overall cable type (single-mode, multimode, etc.).
3. Are color codes the same worldwide?
Mostly, yes. North America follows TIA-598-C, while international markets often reference IEC 60304 — both use similar principles.
4. Can I customize fiber color coding?
Yes. PHILISUN offers custom color coding for enterprise or OEM clients, ensuring easy system identification and better cable management.
5. What happens if fiber colors are mislabeled?
Incorrect labeling can cause serious network confusion, splicing errors, and downtime. Always verify color consistency during cable manufacturing and testing.
Conclusion
The fiber optic color code is more than just a visual guide — it’s the foundation of efficient, scalable, and safe fiber network design.
By following international standards, network engineers can ensure consistent performance and easier maintenance across complex infrastructures.
PHILISUN continues to deliver precision-engineered fiber optic cables that meet these standards, combining reliability, color accuracy, and professional labeling for every project — from small office LANs to hyperscale data centers.
Contact PHILISUN today to explore our range of single-mode, multimode, and hybrid fiber cables — all built with industry-standard color compliance, custom labeling, and guaranteed performance.