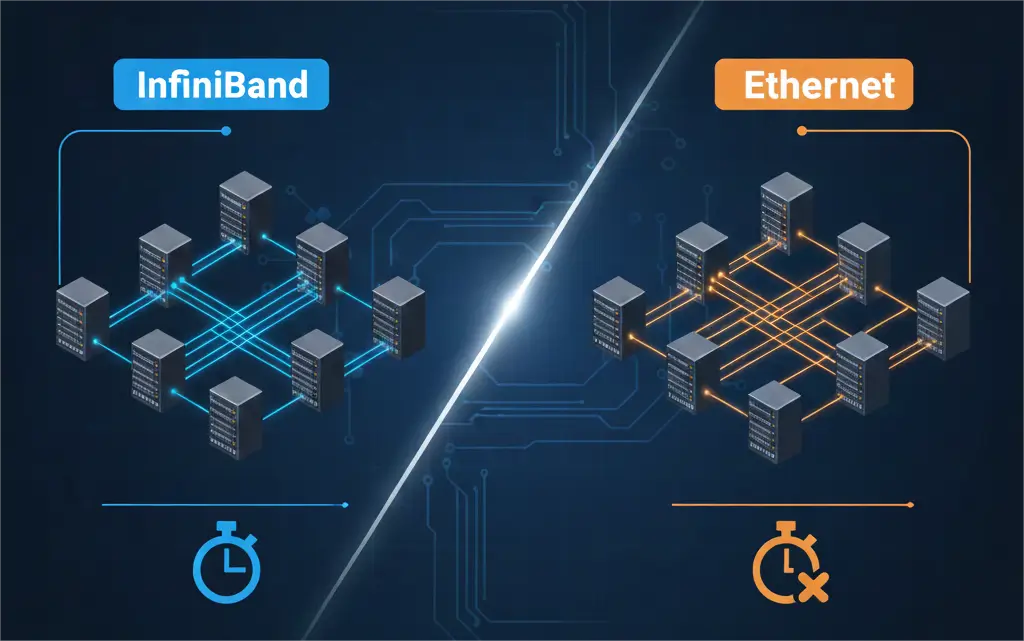
In AI and HPC, every microsecond is precious. Network latency critically affects NVIDIA GPU communication and distributed workload efficiency. Low latency isn’t just an advantage; it’s essential for peak performance. Two leading network technologies, InfiniBand and Ethernet, offer high bandwidth. However, their approaches to latency differ fundamentally.
For data center architects, understanding InfiniBand vs Ethernet latency is crucial. This knowledge guides strategic decisions for AI and HPC clusters. At PHILISUN, we know your NVIDIA GPUs’ true power relies on an uncompromised network. This guide compares InfiniBand and Ethernet’s latency characteristics.
Why Low Latency Fuels AI & HPC
Modern AI and HPC workloads are highly parallel and interconnected. GPUs demand instant data. Delays in data movement bottleneck even the fastest processors, causing costly idle cycles.
Latency’s Direct Performance Impact
- Accelerating Collective Operations
AI training requires GPUs to share and synchronize results. Operations like all-reduce demand rapid, synchronized transfers. High latency bottlenecks these critical processes.
- Preventing GPU Starvation
Expensive NVIDIA GPUs must stay busy. High network latency forces GPUs to wait for data, leading to underutilization. Low latency ensures continuous data flow.
- Enabling Seamless Scalability
Latency limits cluster scaling. More network hops add cumulative delay. Ultra-low-latency fabrics are essential for building larger, tightly coupled AI clusters.
InfiniBand: Engineered for Ultra-Low Latency
InfiniBand’s design prioritizes ultra-low latency. It achieves this through specialized architectural choices, distinguishing it from general-purpose networking.
InfiniBand’s Latency Advantage
Streamlined Protocol Stack
InfiniBand uses a lean protocol, bypassing complex TCP/IP layers. This means fewer processing steps, reducing latency from application to wire.
Native Hardware Offload (RDMA)
RDMA enables direct memory-to-memory data transfers between machines. It bypasses CPU/OS involvement, significantly reducing software overhead and latency.
Inherently Lossless Fabric
InfiniBand is designed to be lossless, preventing packet drops with credit-based flow control. Avoiding retransmissions is key to consistent low latency.
Integrated Congestion Management
InfiniBand fabrics have hardware-accelerated congestion management. This proactively detects and reacts to bottlenecks, ensuring consistent low latency under heavy load.
InfiniBand Latency in Practice
Typical InfiniBand end-to-end latency is sub-microsecond. A single switch hop adds only a few hundred nanoseconds. This makes InfiniBand ideal for tightly coupled AI/HPC workloads.
Ethernet with RoCE: Bridging the Divide
Standard Ethernet historically had higher latency. However, RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE v2) has significantly closed this gap. RoCE v2 layers InfiniBand’s RDMA over standard Ethernet.
RoCE’s Approach to Lower Latency
RDMA over Ethernet (RoCE v2)
RoCE v2 brings RDMA to Ethernet, bypassing CPU/OS for direct memory transfers. This substantially reduces application-level latency.
CEE for Lossless Transport
For optimal RoCE, Ethernet needs Priority Flow Control (PFC) to prevent packet drops and Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) for congestion management. These CEE features ensure near-lossless performance.
Network Design is Key
Achieving low latency with RoCE requires careful network design, proper switch buffering, and precise traffic prioritization.
Ethernet (RoCE) Latency in Practice
Well-tuned RoCE v2 networks achieve few-microsecond latencies. This is slightly higher than native InfiniBand but a vast improvement over standard TCP/IP. Latency can vary more with RoCE, depending on hardware and configuration.
InfiniBand vs Ethernet: Direct Comparison
Comparing InfiniBand and Ethernet (with RoCE) highlights their distinct strengths and trade-offs regarding latency.
Core Latency Differences
| Feature | InfiniBand | Ethernet (with RoCE) |
| Protocol Stack | Lean, purpose-built | Multi-layered (MAC/IP overhead) |
| RDMA Implementation | Native, hardware-integrated | Layered over Ethernet |
| Lossless Transport | Inherently lossless (credit-based) | Achieved via PFC/ECN (requires careful tuning) |
| Congestion Management | Hardware-accelerated, integrated | Software/switch-dependent, less deterministic |
| Typical Latency | Sub-microsecond | Few-microseconds |
Performance Considerations
InfiniBand’s leaner stack and native RDMA offer a consistent, ultra-low latency edge. RoCE provides excellent performance, but its latency can be more variable under heavy loads without precise tuning.
PHILISUN’s Strategic Advantage: Precision Interconnects
PHILISUN understands latency’s critical impact on NVIDIA AI/HPC. We engineer and provide ultra-low latency interconnect solutions at the physical layer, ensuring your network never bottlenecks performance.
Our Solutions for Minimal Latency
Engineered for Minimal Delay
Our 200G, 400G, and 800G optical transceivers use advanced opto-electronics. They minimize latency during electrical-to-optical conversion.
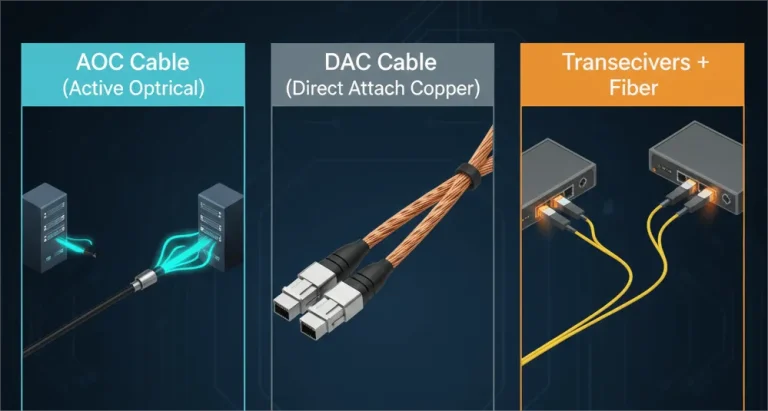
High-Performance AOCs and DACs
For short distances, our AOCs and DACs offer direct, low-loss, and inherently low-latency connections. They minimize signal delay within racks.
Rigorous Performance Validation
Every PHILISUN product undergoes stringent testing for latency and reliability with actual NVIDIA hardware. This ensures flawless operation in demanding AI environments.
Optimized for Both Fabrics
Our products support both InfiniBand and high-performance Ethernet (RoCE). We provide the right physical interconnect for your chosen protocol.
Conclusion: Smart Interconnect Choices for AI & HPC
The InfiniBand vs Ethernet latency decision is strategic. InfiniBand offers the absolute lowest, most predictable latency, ideal for tightly coupled workloads. Ethernet with RoCE provides excellent performance, offering flexibility and broader ecosystem support for many AI tasks.
The optimal choice depends on your specific NVIDIA AI workload, budget, and scalability. PHILISUN supports both paths. We provide ultra-low latency, high-bandwidth interconnects. These solutions empower your NVIDIA AI infrastructure, ensuring peak efficiency.
Partner with PHILISUN to eliminate network latency as a barrier to innovation.