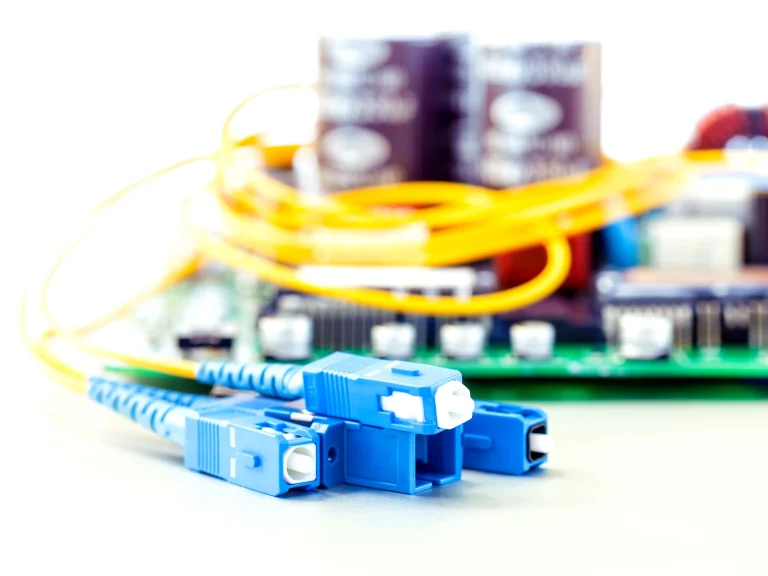
A patch cord is a short cable designed to connect network devices and transmit data signals efficiently. It forms a crucial part of structured cabling systems, ensuring fast, stable, and secure communication between switches, patch panels, and servers.
Depending on the application, patch cords can be copper-based or fiber optic, each optimized for different transmission needs and environments.
What Is a Patch Cord?
A patch cord, sometimes called a patch cable or jumper, connects two electronic or optical devices to enable data transfer. Typically, patch cords are factory-terminated and pre-tested to ensure consistent performance and easy installation.
They are widely used in telecommunication rooms, data centers, and enterprise networks, where reliable connectivity and flexibility are essential.
Patch Cord vs. Network Cable
Though both carry signals, patch cords and network cables serve different purposes.
| Category | Patch Cord | Network Cable |
| Usage | Device-to-device connection | Permanent cabling inside walls or conduits |
| Structure | Factory-terminated, stranded wire | Solid-core for fixed installations |
| Length | Short (0.5–10 m) | Long (10–100 m) |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible | Rigid |
| Typical Connector | RJ45 or MPO | RJ45 or punch-down termination |
Patch cords are ideal for connecting active devices, while network cables make up the permanent backbone of the infrastructure.
Types of Patch Cords
Patch cords are classified by transmission medium, performance, and connector type. The two primary categories are copper patch cords and fiber optic patch cords.
| Type | Material | Signal Medium | Common Application |
| Copper Patch Cord | Twisted-pair copper | Electrical | LANs, small offices |
| Fiber Optic Patch Cord | Glass or plastic fiber | Optical (light) | Data centers, telecom systems |
Copper Patch Cord
Copper patch cords are used primarily in Ethernet networks. They consist of twisted pairs that help reduce electromagnetic interference. Copper cords are rated by Category (CAT) standards that define speed and bandwidth.
Common Ethernet Categories
| Category | Maximum Speed | Bandwidth | Distance | Shielding Option | Typical Use |
| Cat5e | 1 Gbps | 100 MHz | 100 m | UTP / STP | Standard LAN environments |
| Cat6 | 10 Gbps (≤55 m) | 250 MHz | 100 m | UTP / STP | High-speed office networks |
| Cat6A | 10 Gbps | 500 MHz | 100 m | UTP / STP | Enterprise cabling systems |
| Cat7 | 10 Gbps | 600 MHz | 100 m | S/FTP | Data centers |
| Cat7A | 10+ Gbps | 1000 MHz | 100 m | S/FTP | Industrial and backbone cabling |
Higher-category cables provide greater performance and signal integrity. Shielded types (STP or S/FTP) are recommended for electrically noisy environments.
Fiber Optic Patch Cord
Fiber patch cords are used where higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances are required. They transmit data through light signals, providing faster and interference-free communication.
| Type | Core Size | Transmission Distance | Typical Use |
| Single-Mode (SM) | ~9 μm | Up to 40 km or more | Long-distance transmission |
| Multi-Mode (MM) | 50 μm or 62.5 μm | Up to 550 m | Short-range connections |
Single-mode cords (yellow) are used for long-haul communication, while multi-mode cords (orange or aqua) serve short interconnections within buildings.
Common Connector Types
| Connector Type | Used For | Description |
| RJ45 | Copper Ethernet | Standard connector for LANs |
| LC / SC / ST | Fiber optic | Compact, low-loss connectors |
| MPO/MTP | High-density fiber | Supports 8–24 fibers per interface |
Connector selection impacts performance, maintenance ease, and scalability. MPO/MTP connectors are especially popular in high-density environments.
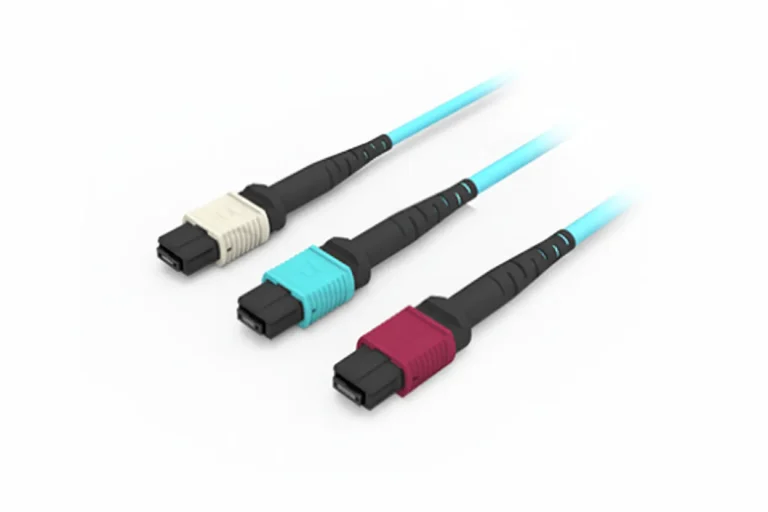
MPO Patch Cord in High-Density Networks
MPO (Multi-Fiber Push-On) patch cords integrate multiple fibers into one connector, enabling rapid deployment and compact cable management. They are the foundation of 40G/100G/400G Ethernet systems, supporting data centers where efficiency and scalability are vital.
MPO patch cords simplify installation, reduce rack space, and prepare networks for future upgrades.
Example: PHILISUN’s SM OS2 MPO Jumpers
PHILISUN, established in 2001, specializes in advanced fiber optic solutions. Its SM OS2 MPO Jumpers feature high-density design, low insertion loss, and excellent single-mode performance, ideal for data centers and telecom backbones. With 8-, 12-, and 24-core options, they provide reliable and flexible connectivity for high-speed network environments.
How to Choose the Right Patch Cord
When choosing a patch cord, consider:
- Transmission Type – Copper for short distances, fiber for high-speed or long-range use.
- Connector Compatibility – Match the device interfaces (RJ45, LC, or MPO).
- Cable Category or Mode – Higher-rated cables ensure better performance.
- Length and Flexibility – Choose lengths that reduce slack while allowing movement.
- Compliance – Ensure the product meets ISO/IEC or TIA/EIA standards.
The right patch cord enhances performance, minimizes signal loss, and ensures long-term network stability.
Conclusion
Patch cords are indispensable components in both copper and fiber networks, connecting devices and ensuring efficient data transfer. By understanding their types, categories, and applications, network professionals can select cables that balance performance, flexibility, and reliability.
For organizations seeking quality and precision, PHILISUN‘s patch cord solutions offer dependable performance for today’s high-speed communication environments.