Network for NVIDIA AI Cluster H100 & H800: Interconnect Guide
In the race to develop advanced AI models, NVIDIA GPUs like the H100 and H800 are the undisputed compute powerhouses. However, their true potential is unleashed only when they are connected by an equally powerful, low-latency, and high-bandwidth network fabric. Without robust interconnects, even the most formidable GPUs will starve for data, leading to underutilized resources and stalled progress.
This guide is designed for network architects and data center engineers tasked with building or upgrading NVIDIA-powered AI and High-Performance Computing (HPC) clusters. We won’t delve into the specifics of GPU chip architecture (you can find an excellent technical deep-dive on NVIDIA H800 vs H100 here). Instead, our focus is squarely on the external networking requirements of these formidable machines – specifically, the critical role of high-speed optical transceivers, Active Optical Cables (AOCs), and Direct Attach Copper (DAC) in building a resilient and performant AI network.
Why AI Demands a Specialized Network Fabric
AI and HPC workloads differ significantly from traditional data center traffic. They are characterized by:
- Massive Data Movement: Training large models involves terabytes, even petabytes, of data moving between GPUs, memory, and storage.
- Collective Communications: GPUs frequently need to exchange information simultaneously (e.g., all-reduce operations), requiring minimal latency and jitter across the entire fabric.
- Burstiness: Data transfer patterns can be highly bursty, demanding networks that can handle sudden, intense spikes in traffic without congestion.
A traditional enterprise network, optimized for diverse application traffic and general web services, often cannot meet these stringent demands. AI requires a dedicated, purpose-built interconnect fabric.
Understanding NVIDIA’s Network Interfaces: The Gateway to Your GPUs
NVIDIA GPUs and specialized DPU (Data Processing Unit) network cards are the physical points where your network fabric connects. Key NVIDIA components and their interfaces include:
- NVIDIA ConnectX® DPUs: These intelligent network adapters (e.g., ConnectX-7) are installed in GPU servers, providing high-bandwidth external connectivity. They typically feature QSFP-DD or OSFP ports, supporting 200G, 400G, or even 800G speeds.
- NVIDIA DGX™ Systems: Integrated AI supercomputing nodes (e.g., NVIDIA DGX H100) combine multiple GPUs and internal NVLink with external high-speed network interfaces, often multiple OSFP ports for compute and storage fabrics.
- NVIDIA InfiniBand & Ethernet Switches: These core fabric devices (e.g., NVIDIA Quantum-2 InfiniBand Switches) also present QSFP-DD or OSFP ports to connect the entire cluster.
PHILISUN Insight: Regardless of the NVIDIA component, the physical interface form factors (QSFP-DD, OSFP) are standardized. This is where PHILISUN’s MSA-compliant optical transceivers and cables come in, providing the crucial physical link.
InfiniBand vs. RoCE (Ethernet): Choosing Your AI Protocol
NVIDIA offers two primary high-performance networking protocols for AI clusters, each with distinct advantages:
InfiniBand (IB)
- Overview: InfiniBand is a dedicated, lossless, low-latency serial interconnect originally designed for HPC. It’s renowned for its Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) capabilities, allowing GPUs to directly access memory on other GPUs or hosts without CPU intervention, minimizing latency.
- NVIDIA’s Role: Through its acquisition of Mellanox, NVIDIA is the leading proponent of InfiniBand. According to NVIDIA’s official stance on InfiniBand, it provides “guaranteed bandwidth, ultra-low latency, and in-network computing capabilities vital for scale-out AI training.”
- Key Features: Native hardware offload for collective operations, no-drop packet forwarding (lossless fabric), and advanced congestion control.
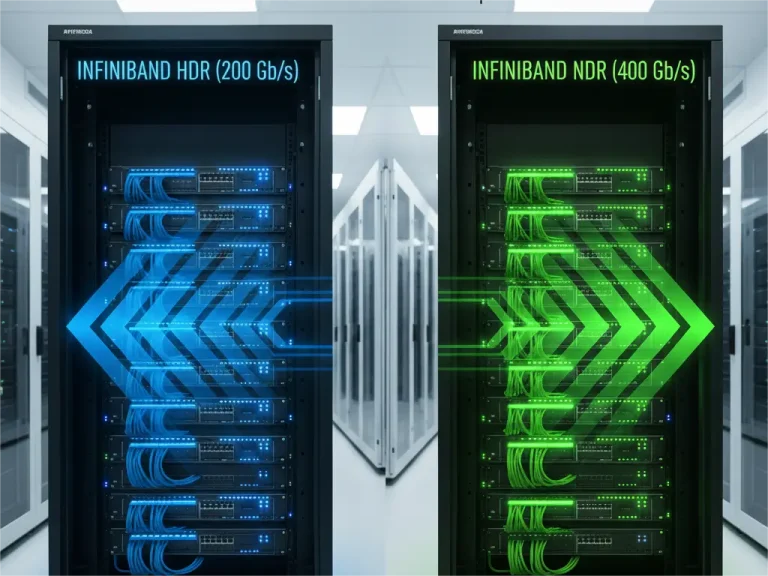
- Physical Layer: InfiniBand utilizes common form factors like QSFP-DD and OSFP, operating at speeds like HDR (200G) and NDR (400G).
- PHILISUN Interconnects for InfiniBand: Our 200G, 400G, and 800G OSFP/QSFP-DD optical transceivers, AOCs, and DACs are fully compliant with InfiniBand HDR and NDR specifications, ensuring seamless integration with NVIDIA Quantum and Quantum-2 InfiniBand switches.
RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE v2)
- Overview: RoCE v2 allows RDMA to run over standard Ethernet networks, leveraging its ubiquitous infrastructure. While not inherently lossless, RoCE v2 relies on advanced Ethernet features to achieve near-lossless performance.
- NVIDIA’s Role: NVIDIA’s Spectrum-X Ethernet Platform is a key offering here, designed to bring InfiniBand-like performance to an Ethernet fabric. NVIDIA states that Spectrum-X aims to deliver “predictable performance, low latency, and high bandwidth for AI workloads on Ethernet.”
- Key Features: Requires careful configuration of Priority Flow Control (PFC) and Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) on Ethernet switches to prevent packet drops and maintain low latency for RDMA traffic.
- Physical Layer: Uses standard Ethernet optical modules and cables, operating at speeds like 200G, 400G, and emerging 800G.
- PHILISUN Interconnects for RoCE Ethernet: Our IEEE 802.3-compliant 200G, 400G, and 800G OSFP/QSFP-DD optical transceivers, AOCs, and DACs are optimized for high-performance Ethernet environments, providing the robust physical layer needed for demanding RoCE fabrics.
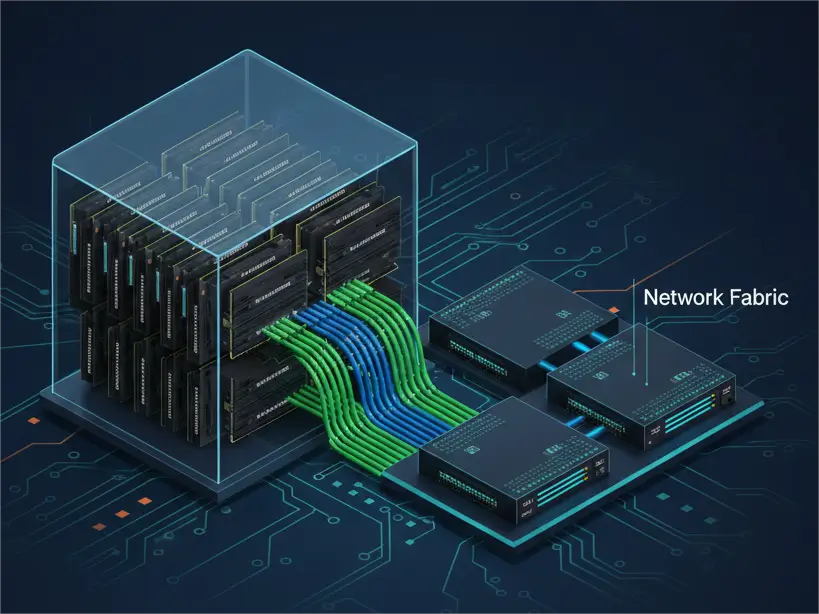
The Interconnect Arsenal: Choosing the Right PHY for Your NVIDIA Cluster
The choice of physical interconnect (PHY) depends on distance, budget, and specific performance requirements within your NVIDIA AI cluster.
Direct Attach Copper (DAC) & Active Copper Cables (ACC/AEC)
- Application: Ideal for ultra-short distances, typically within the same server rack (e.g., connecting a ConnectX-7 DPU in a server to a Top-of-Rack switch).
- Advantages: Lowest latency, lowest cost, near-zero power consumption.
- PHILISUN Offering: High-quality 200G, 400G, and 800G QSFP-DD and OSFP DACs/ACCs, pre-tested for error-free operation with NVIDIA hardware.
Active Optical Cables (AOCs)
- Application: Short to medium distances, typically connecting adjacent racks or racks within the same row (e.g., from a DGX H100 node to a spine switch in the next rack). Distances up to ~30-50 meters for 400G.
- Advantages: Lighter and more flexible than DACs (improving rack airflow and management), longer reach, plug-and-play simplicity (no separate transceivers or fiber cleaning required).
- PHILISUN Offering: A comprehensive range of MSA-compliant AOCs. Our AOCs are specifically designed for the stringent requirements of AI clusters, offering low power, high reliability, and available in custom lengths for optimal cable management.
Optical Transceivers + Fiber Optic Cabling
- Application: Long distances, connecting AI pods to the data center core, or linking distributed AI clusters across a campus or metropolitan area.
- Advantages: Highest reach, ultimate flexibility for various fiber types.
- Key Transceiver Types for NVIDIA Clusters:
- SR8 (Short Reach Multimode): Uses parallel multimode fiber (e.g., MPO-16 or 2x MPO-12). Per IEEE 802.3db, suitable for reaches up to ~100m over OM4/OM5 fiber. Ideal for high-density intra-data center links.
- DR4/FR4 (Datacenter/Far Reach Single-Mode): Leverages parallel or wavelength-multiplexed single-mode fiber for longer reaches (500m – 2km). These transceivers adhere to IEEE 802.3cu and 100G Lambda MSA specifications, essential for building larger, more distributed AI fabrics.
- PHILISUN Offering: A comprehensive suite of MSA-compliant 400G/800G OSFP and QSFP-DD transceivers (SR8, DR4, FR4). Paired with our high-density Base-8 or Base-16 MPO trunk cabling, we provide a complete, scalable, and high-performance fiber optic solution.
Future-Proofing Your AI Network: Beyond 400G
The pace of AI innovation demands a network that can evolve. As NVIDIA introduces next-generation GPUs (e.g., the Blackwell platform) and 800G/1.6T networking becomes standard, your cabling infrastructure should be ready. Investing in single-mode fiber and modular MPO solutions today ensures an easier upgrade path for future transceiver generations.
Conclusion
Building a high-performance network fabric for NVIDIA AI clusters is a complex task requiring deep technical understanding and reliable, high-quality components. Don’t let your network become the bottleneck for your valuable GPU investments.
At PHILISUN, our engineering team is deeply familiar with the unique demands of AI and HPC networking. We offer a full spectrum of rigorously tested, MSA-compliant, and NVIDIA-compatible optical transceivers, AOCs, and DACs, from 200G to 800G. We provide the physical layer solutions to ensure your NVIDIA H100, H800, A100, and future GPUs communicate at the speed of thought.