
CWDM vs DWDM: Which Technology Should You Choose for Your Network?
CWDM is cheaper for short-haul access networks due to uncooled lasers (20nm spacing), while DWDM offers greater capacity and distance (>80km) for core links.

CWDM is cheaper for short-haul access networks due to uncooled lasers (20nm spacing), while DWDM offers greater capacity and distance (>80km) for core links.

Fiber optic speed is defined by the transceivers and cables used. We explain data rates from 10G to 800G, the role of modulation (PAM4), and why high-quality AOCs are key.

Use the technician's 7-step protocol to clean a fiber optic connector, covering dry/wet methods, MPO specialization, and IEC 61300-3-35 inspection to eliminate 400G+ link failures.

Intel Gaudi 3 features 24 integrated 200G RoCE ports for massive scalability. Learn the required QSFP56 AOC/DAC cabling and network topology for a stable Gaudi 3 cluster.

Intel SFP+ transceivers require custom coding for X520/X710 NICs. Learn how to bypass OEM lockouts and ensure 100% stability with PHILISUN’s tested modules.

LC offers high density, SC is push-pull for ease of use, and MPO bundles 12+ fibers for 40G/100G speed. Find your ideal connector here.

Intel NICs (X710/E810) use firmware to lock out optics. This guide explains the root cause of "uncertified module" errors and provides 5 crucial compatibility fixes.

SFP vs SFP+ vs QSFP vs QSFP28: The key difference is speed and lane count (1G/10G/25G vs 40G/100G). SFP is 1G, SFP+ is 10G, SFP28 is 25G (all 1 lane). QSFP+ is 4x10G, QSFP28 is 4x25G (4 lanes).
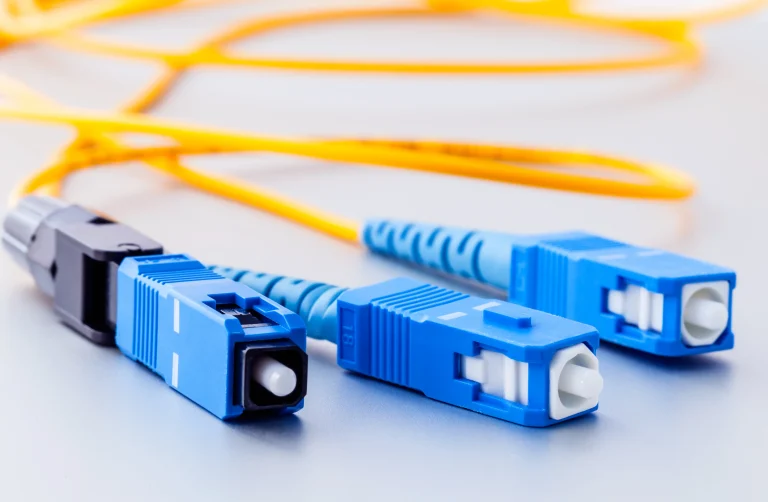
A Fiber Jumper (patch cable) is a short fiber cable used to connect devices or distribution panels. Learn the 7 specs (IL, RL, MPO) essential for high-speed network reliability.
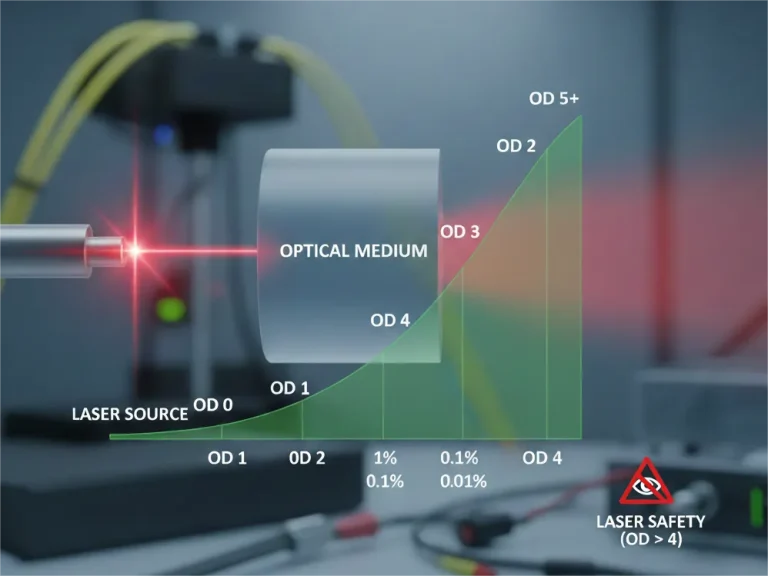
Optical Density (OD) is the logarithmic measure of light attenuation. It determines how much power a medium absorbs. Critical for laser safety, filters, and PHILISUN's high-precision optics.