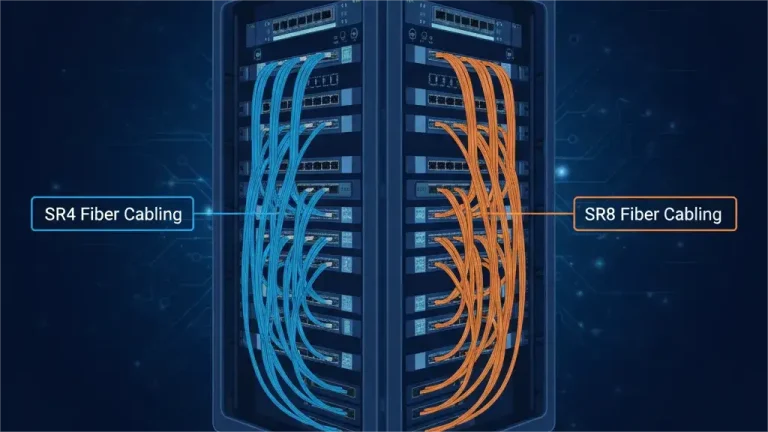
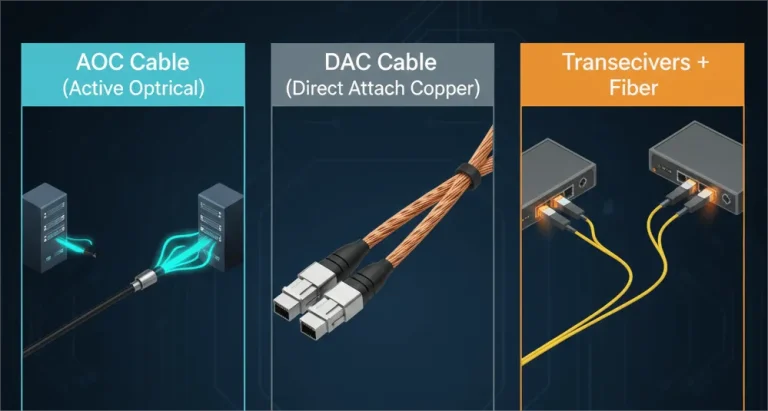
SR4 vs SR8 Fiber Cabling: A Complete Guide for 100G, 400G & 800G Networks
Compare SR4 vs SR8 fiber cabling for 100G, 400G, and 800G networks. Learn about MPO-12 vs MPO-16, cabling costs, upgrade paths, and how PHILISUN optimizes SR4/SR8 deployments with high-quality parallel optic solutions.